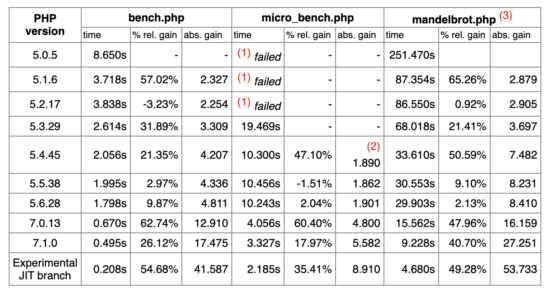
Last modified on January 5th, 2021.
Increase user engagement with your eCommerce website to see your sales leap forward. There are multiple tools like rating, comments, queries, and wishlist to increase user engagement.
A persistent shopping cart (over different user sessions) allows user’s to store and earmark products for future purchase. A wishlist helps to do that in a better organized way.
A wishlist is an eCommerce website feature that helps the users to manage list of products that the user wants to purchase later. It also allows maintaining a “yet to purchase” list of items. This feature will increase your eCommerce business conversion rate.
The eCommerce application providers follow types of mechanisms to implement this feature. The terminology may differ from application to application. Example: Save for future, wishlist, favorites and more.
This example uses a simple way of implementation with a straight-forward code. It user database to manage users wishlist.
You can integrate the wishlist module of this example for your online shopping cart software.
What is inside?
- About this example
- File structure
- eCommerce wishlist view in HTML
- jQuery AJAX to add/remove wishlist items
- PHP code to create and manage eCommerce wishlist
- Database script
- E-Commerce wishlist example output
About this example
This example code is with the feature to create users’ wishlist for eCommerce software. It will give a clean and simple code to add the eCommerce wishlist feature.
I have created a simple php shopping cart script before in a previous tutorial. This example is an enhanced version of the simple shopping cart with a wishlist.
This code will allow users to add products to their wishlist from the product gallery. Also, it allows to unset an item to remove from the wishlist.
The wishlist gallery items are dynamic from the database. The add/remove actions will change the wishlist data in the database.
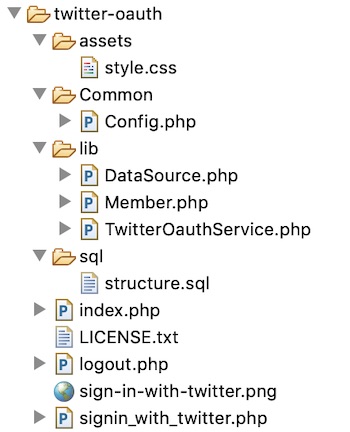
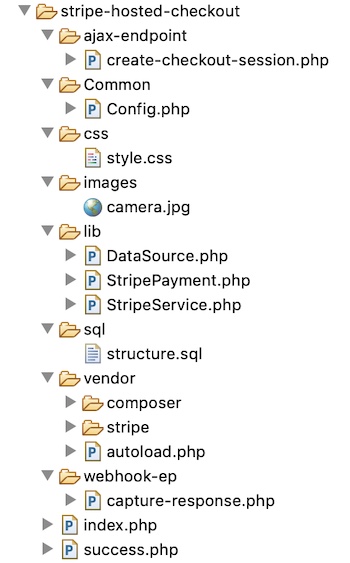
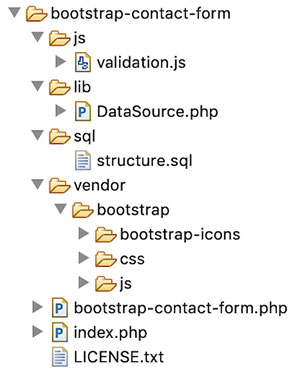
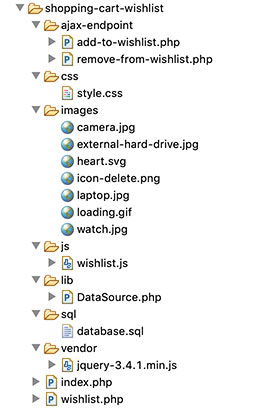
File Structure
This diagram shows the files created for this example. It has an organized structured code of eCommerce wishlist implementation.
It shows the view files, libraries and application assets separated in a proper manner.
The image folder contains application icons. Also, it includes images to display the product and wishlist gallery.
This tutorial has a downloadable source at the end with the database script.
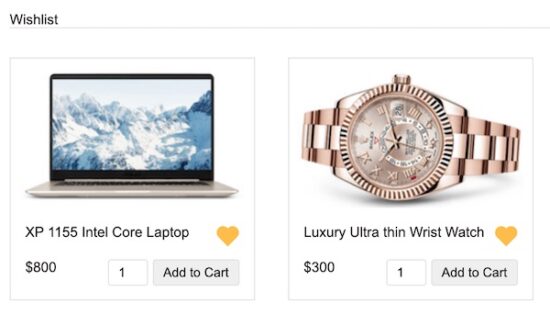
eCommerce wishlist view in HTML
This example has two types of galleries. One is a regular eCommerce product gallery and the other is a users’ wishlist gallery.
This example uses a hard-coded member id to get the users’ wishlist from the database. It may adopt a login module to get the id from the session.
The product gallery is on the landing page, below the shopping cart list view. This page includes the navigation link to go to the eCommerce application wishlist.
The product gallery has the line heart icon in each tile. It will add the items to the wishlist on its click event. After adding, the wishlist gallery shows the filled heart on the particular tile.
The filled heart icon on-click event will remove the items from the wishlist.
index.php
<?php
session_start();
require_once __DIR__ . "/lib/DataSource.php";
$db_handle = new DataSource(); $query = 'SELECT * FROM tbl_whish_list JOIN tblproduct ON tblproduct.id = tbl_whish_list.product_id ORDER BY tbl_whish_list.product_id ASC'; $whish_array = $db_handle->select($query);
$whish_array_pid = array();
if (! empty($whish_array)) { foreach ($whish_array as $z => $value) { $whish_array_pid[] = $whish_array[$z]['product_id']; }
}
if (! empty($_GET["action"])) { switch ($_GET["action"]) { case "add": if (! empty($_POST["quantity"])) { $query = 'SELECT * FROM tblproduct WHERE code= ? '; $paramType = 's'; $paramValue = array( $_GET["code"] ); $productByCode = $db_handle->select($query, $paramType, $paramValue); $itemArray = array( $productByCode[0]["code"] => array( 'name' => $productByCode[0]["name"], 'code' => $productByCode[0]["code"], 'quantity' => $_POST["quantity"], 'price' => $productByCode[0]["price"], 'image' => $productByCode[0]["image"] ) ); if (! empty($_SESSION["cart_item"])) { if (in_array($productByCode[0]["code"], array_keys($_SESSION["cart_item"]))) { foreach ($_SESSION["cart_item"] as $k => $v) { if ($productByCode[0]["code"] == $k) { if (empty($_SESSION["cart_item"][$k]["quantity"])) { $_SESSION["cart_item"][$k]["quantity"] = 0; } $_SESSION["cart_item"][$k]["quantity"] += $_POST["quantity"]; } } } else { $_SESSION["cart_item"] = array_merge($_SESSION["cart_item"], $itemArray); } } else { $_SESSION["cart_item"] = $itemArray; } } break; case "remove": if (! empty($_SESSION["cart_item"])) { foreach ($_SESSION["cart_item"] as $k => $v) { if ($_GET["code"] == $k) unset($_SESSION["cart_item"][$k]); if (empty($_SESSION["cart_item"])) unset($_SESSION["cart_item"]); } } break; case "empty": unset($_SESSION["cart_item"]); break; }
}
?>
<HTML>
<HEAD>
<TITLE>Simple PHP Shopping Cart</TITLE>
<link href="css/style.css" type="text/css" rel="stylesheet" />
</HEAD>
<BODY> <div id="shopping-cart"> <div class="txt-heading">Shopping Cart</div> <a id="btnEmpty" href="index.php?action=empty">Empty Cart</a>
<?php
if (isset($_SESSION["cart_item"])) { $total_quantity = 0; $total_price = 0; ?>
<table class="tbl-cart" cellpadding="10" cellspacing="1"> <tbody> <tr> <th class="text-left">Name</th> <th class="text-left">Code</th> <th class="text-right">Quantity</th> <th class="text-right">Unit Price</th> <th class="text-right">Price</th> <th class="text-center">Remove</th> </tr>
<?php foreach ($_SESSION["cart_item"] as $item) { $item_price = $item["quantity"] * $item["price"]; ?> <tr> <td><img src="<?php echo $item["image"]; ?>" class="cart-item-image" /><?php echo $item["name"]; ?></td> <td><?php echo $item["code"]; ?></td> <td class="text-right"><?php echo $item["quantity"]; ?></td> <td class="text-right"><?php echo "$ ".$item["price"]; ?></td> <td class="text-right"><?php echo "$ ". number_format($item_price,2); ?></td> <td class="text-center"><a href="index.php?action=remove&code=<?php echo $item["code"]; ?>" class="btnRemoveAction"><img src="images/icon-delete.png" alt="Remove Item" /></a></td> </tr> <?php $total_quantity += $item["quantity"]; $total_price += ($item["price"] * $item["quantity"]); } ?> <tr> <td colspan="2" align="right">Total:</td> <td align="right"><?php echo $total_quantity; ?></td> <td align="right" colspan="2"><strong><?php echo "$ ".number_format($total_price, 2); ?></strong></td> <td></td> </tr> </tbody> </table> <?php
} else { ?>
<div class="no-records">Your Cart is Empty</div>
<?php
}
?>
</div> <div id="product-grid"> <div class="txt-heading">Products</div> <?php
$query = 'SELECT * FROM tblproduct ORDER BY id ASC';
$product_array = $db_handle->select($query);
if (! empty($product_array)) { foreach ($product_array as $key => $value) { ?> <div class="product-item"> <form method="post" action="index.php?action=add&code=<?php echo $product_array[$key]["code"]; ?>"> <div class="product-image"> <img src="<?php echo $product_array[$key]["image"]; ?>"> </div> <div class="product-tile-footer"> <div class="product-title"><?php echo $product_array[$key]["name"]; ?> <?php if (in_array($product_array[$key]["id"], $whish_array_pid)) { ?> <span data-pid="<?php echo $product_array[$key]["id"]; ?>" class="heart" onclick="removeFromWishlist(this)" title="Remove from wishlist"> <svg xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" width="24" height="24" viewBox="0 0 24 24" fill="none" stroke-width="2" stroke-linecap="round" stroke-line join="round" stroke="currentColor" class="feather feather-heart color-filled"> <path d="M20.84 4.61a5.5 5.5 0 0 0-7.78 0L12 5.67l-1.06-1.06a5.5 5.5 0 0 0-7.78 7.78l1.06 1.06L12 21.23l7.78-7.78 1.06-1.06a5.5 5.5 0 0 0 0-7.78z"></path></svg><img src="images/loading.gif" id="loader"> </span> <?php } else { ?> <span data-pid="<?php echo $product_array[$key]["id"]; ?>" class="heart" onclick="addToWishlist(this)" title="Add to wishlist"> <svg xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" width="24" height="24" viewBox="0 0 24 24" fill="none" stroke-width="2" stroke-linecap="round" stroke-line join="round" stroke="currentColor" class="feather feather-heart"> <path d="M20.84 4.61a5.5 5.5 0 0 0-7.78 0L12 5.67l-1.06-1.06a5.5 5.5 0 0 0-7.78 7.78l1.06 1.06L12 21.23l7.78-7.78 1.06-1.06a5.5 5.5 0 0 0 0-7.78z"></path></svg><img src="images/loading.gif" id="loader"> </span> <?php } ?> </div> <div class="product-price"><?php echo "
quot;.$product_array[$key]["price"]; ?></div> <div class="cart-action"> <input type="text" class="product-quantity" name="quantity" value="1" size="2" /><input type="submit" value="Add to Cart" class="btnAddAction" /> </div> </div> </form> </div> <?php }
}
?> </div> <div id="shopping-cart"> <a id="whishlist" href="wishlist.php">Show My Wishlist</a> </div> <script type="text/javascript" src="vendor/jquery-3.4.1.min.js"></script> <script type="text/javascript" src="js/wishlist.js"></script>
</BODY>
</HTML>
wishlist.php
<?php
require_once __DIR__ . "/lib/DataSource.php";
$db = new DataSource();
?>
<HTML>
<HEAD>
<TITLE>Simple PHP Shopping Cart</TITLE>
<link href="css/style.css" type="text/css" rel="stylesheet" />
</HEAD>
<BODY> <div id="shopping-cart"> <div class="whishlist-cntr"> <div class="txt-heading">Wishlist</div> <div id="whishlist-grid"> <?php $query = 'SELECT * FROM tbl_whish_list JOIN tblproduct ON tblproduct.id = tbl_whish_list.product_id'; $whish_array = $db->select($query); if (! empty($whish_array)) { foreach ($whish_array as $key => $value) { ?> <div class="product-item"> <form method="post" action="index.php?action=add&code=<?php echo $whish_array[$key]["code"]; ?>"> <div class="product-image"> <img src="<?php echo $whish_array[$key]["image"]; ?>"> </div> <div class="product-tile-footer"> <div class="product-title"><?php echo $whish_array[$key]["name"]; ?> <span data-pid="<?php echo $whish_array[$key]["product_id"]; ?>" class="heart" onclick="removeFromWishlist(this)" title="Add to wish list"> <svg xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" width="24" height="24" viewBox="0 0 24 24" fill="none" stroke-width="2" stroke-linecap="round" stroke-line join="round" stroke="currentColor" class="feather feather-heart color-filled"> <path d="M20.84 4.61a5.5 5.5 0 0 0-7.78 0L12 5.67l-1.06-1.06a5.5 5.5 0 0 0-7.78 7.78l1.06 1.06L12 21.23l7.78-7.78 1.06-1.06a5.5 5.5 0 0 0 0-7.78z"></path></svg> <img src="images/loading.gif" id="loader"> </span> </div> <div class="product-price"><?php echo "
quot;.$whish_array[$key]["price"]; ?></div> <div class="cart-action"> <input type="text" class="product-quantity" name="quantity" value="1" size="2" /><input type="submit" value="Add to Cart" class="btnAddAction" /> </div> </div> </form> </div> <?php }
}
?>
</div> </div> </div> <script type="text/javascript" src="vendor/jquery-3.4.1.min.js"></script> <script type="text/javascript" src="js/wishlist.js"></script>
</BODY>
</HTML>
jQuery AJAX to add / remove wishlist items
This JavaScript file contains the functions to process the AJAX request to add/remove wishlist items.
The addToWishList() function gets the product id from the HTML data attribute. This id is a request param to perform the add action in the server.
Similarly, the removeFromWishlist() function calls the server URL to execute the delete query on the wishlist database.
Both the AJAX functions manipulate UI elements to give a seamless and very good user experience on these actions.
js/wishlist.js
function addToWishlist(obj) { var p_id = $(obj).data("pid"); $(obj).find("svg").hide(); $(obj).find("img").show(); $.ajax({ url : "ajax-endpoint/add-to-wishlist.php", type : "POST", data : 'p_id=' + p_id, success : function(data) { $(obj).find("svg").show(); $(obj).find("img").hide(); if (data > 0) { markedAsChecked($(obj)); } } });
} function removeFromWishlist(obj) { var p_id = $(obj).data("pid"); $(obj).find("svg").hide(); $(obj).find("img").show(); $.ajax({ url : "ajax-endpoint/remove-from-wishlist.php", type : "POST", data : 'p_id=' + p_id, success : function(data) { if (data > 0) { $(obj).find("svg").show(); $(obj).find("img").hide(); markedAsUnchecked($(obj)); } } });
} function markedAsChecked(obj) { $(obj).find("svg").addClass("color-filled"); $(obj).find("svg").parent().attr("onClick", "removeFromWishlist(this)"); $(obj).find("svg").parent().attr("title", "Remove from wishlist")
} function markedAsUnchecked(obj) { $(obj).find("svg").removeClass("color-filled"); $(obj).find("svg").parent().attr("onClick", "addToWishlist(this)"); $(obj).find("svg").parent().attr("title", "Add to wishlist")
}
PHP code to create and manage wishlist
This section shows the code to move product to or from the eCommerce wishlist.
On clicking the heart icon in the product gallery, the AJAX will call this PHP. This file inserts the selected item to the users’ eCommerce wishlist.
ajax-endpoint/add-to-wishlist.php
<?php
require_once __DIR__ . "/../lib/DataSource.php";
$db_handle = new DataSource();
if (! empty($_POST["p_id"])) { $memberId = 1; $sql = "INSERT INTO tbl_whish_list (product_id, member_id) VALUES (?, ?)"; $paramType = 'ii'; $paramValue = array( $_POST["p_id"], $memberId ); $whishlist_id = $db_handle->insert($sql, $paramType, $paramValue); echo $whishlist_id; exit();
}
?>
On clicking the filled heart icon, it calls the following PHP file. It receives the product id from the request param array.
Based on the product_id it prepares the delete query to remove the item from the user’s wishlist.
ajax-endpoint/remove-from-wishlist.php
<?php
require_once __DIR__ . "/../lib/DataSource.php";
$db_handle = new DataSource();
if (! empty($_POST["p_id"])) { $memberId = 1; $query = "DELETE FROM tbl_whish_list WHERE product_id = ? AND member_id = ?"; $paramType = 'ii'; $paramValue = array( $_POST["p_id"], $memberId ); $affectedRows = $db_handle->delete($query, $paramType, $paramValue); echo $affectedRows;
}
exit();
Database script
Import this database script to run this example in your server. It has the tables to manage shopping cart products, wishlist in the database.
-- -- Database: `ecommerce-wishlist` -- -- -------------------------------------------------------- CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `tblproduct` ( `id` int(8) NOT NULL, `name` varchar(255) NOT NULL, `code` varchar(255) NOT NULL, `image` text NOT NULL, `price` double(10,2) NOT NULL ) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=5 DEFAULT CHARSET=latin1; INSERT INTO `tblproduct` (`id`, `name`, `code`, `image`, `price`) VALUES (1, 'FinePix Pro2 3D Camera', '3DcAM01', 'images/camera.jpg', 1500.00), (2, 'EXP Portable Hard Drive', 'USB02', 'images/external-hard-drive.jpg', 800.00), (3, 'Luxury Ultra thin Wrist Watch', 'wristWear03', 'images/watch.jpg', 300.00), (4, 'XP 1155 Intel Core Laptop', 'LPN45', 'images/laptop.jpg', 800.00); -- -------------------------------------------------------- CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `tbl_whish_list` ( `id` int(11) NOT NULL, `member_id` int(11) NOT NULL, `product_id` int(11) NOT NULL ) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=111 DEFAULT CHARSET=latin1; INSERT INTO `tbl_whish_list` (`id`, `member_id`, `product_id`) VALUES (110, 0, 1); ALTER TABLE `tblproduct` ADD PRIMARY KEY (`id`), ADD UNIQUE KEY `product_code` (`code`); ALTER TABLE `tbl_whish_list` ADD PRIMARY KEY (`id`); ALTER TABLE `tblproduct` MODIFY `id` int(8) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,AUTO_INCREMENT=5; ALTER TABLE `tbl_whish_list` MODIFY `id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,AUTO_INCREMENT=111;
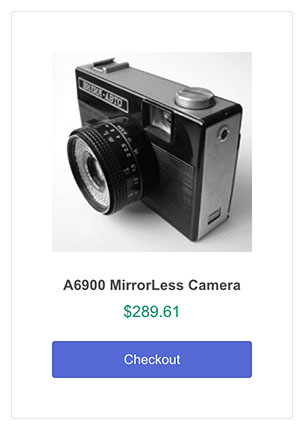
E-Commerce shopping cart wishlist example output
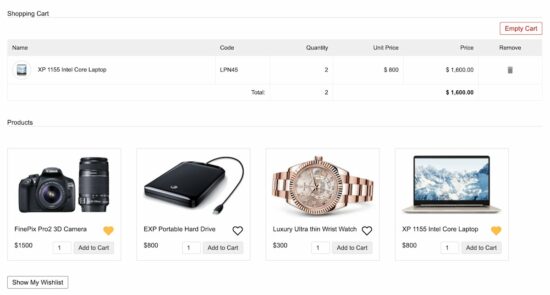
This screenshot shows the eCommerce product gallery below the shopping cart.
Each item in this gallery contains a clickable heart icon to move the item to/from the wishlist.
Items with the filled heart denote that they are on the users’ wishlist.
Conclusion
Thus, we have seen a simple example for creating an eCommerce wishlist for customers.
I hope, it helps you to build a module to support your shopping cart to have this feature to increase the conversion rate.
With straight forward PHP, MySQL code with AJAX, we have seen a reasonably good implementation for getting started.
Since it is with core PHP without any libraries, it is easily adaptable to any eCommerce framework.