
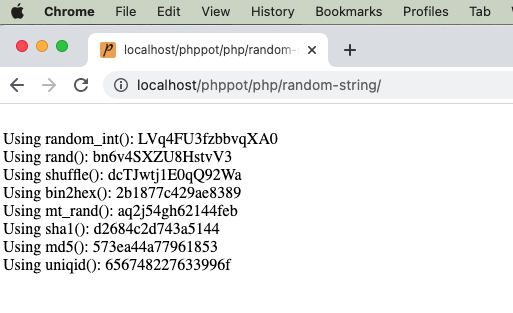
Generating random string token may sound like a trivial work. If you really want something “truly random”, it is one difficult job to do. In a project where you want a not so critical scrambled string there are many ways to get it done.
I present eight different ways of getting a random string token using PHP.
- Using random_int()
- Using rand()
- By string shuffling to generate a random substring.
- Using bin2hex()
- Using mt_rand()
- Using hashing sha1()
- Using hashing md5()
- Using PHP uniqid()
There are too many PHP functions that can be used to generate the random string. With the combination of those functions, this code assures to generate an unrepeatable random string and unpredictable by a civilian user.
1) Using random_int()
The PHP random_int() function generates cryptographic pseudo random integer. This random integer is used as an index to get the character from the given string base.
The string base includes 0-9, a-z and A-Z characters to return an alphanumeric random number.
Quick example
<?php
/** * Uses random_int as core logic and generates a random string * random_int is a pseudorandom number generator * * @param int $length * @return string */
function getRandomStringRandomInt($length = 16)
{ $stringSpace = '0123456789abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ'; $pieces = []; $max = mb_strlen($stringSpace, '8bit') - 1; for ($i = 0; $i < $length; ++ $i) { $pieces[] = $stringSpace[random_int(0, $max)]; } return implode('', $pieces);
}
echo "<br>Using random_int(): " . getRandomStringRandomInt();
?>
2) Using rand()
It uses simple PHP rand() and follows straightforward logic without encoding or encrypting.
It calculates the given string base’s length and pass it as a limit to the rand() function.
It gets the random character with the random index returned by the rand(). It applies string concatenation every time to form the random string in a loop.
<?php
/** * Uses the list of alphabets, numbers as base set, then picks using array index * by using rand() function. * * @param int $length * @return string */
function getRandomStringRand($length = 16)
{ $stringSpace = '0123456789abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ'; $stringLength = strlen($stringSpace); $randomString = ''; for ($i = 0; $i < $length; $i ++) { $randomString = $randomString . $stringSpace[rand(0, $stringLength - 1)]; } return $randomString;
}
echo "<br>Using rand(): " . getRandomStringRand();
?>
3) By string shuffling to generate a random substring.
It returns the random integer with the specified length.
It applies PHP string repeat and shuffle the output string. Then, extracts the substring from the shuffled string with the specified length.
<?php
/** * Uses the list of alphabets, numbers as base set. * Then shuffle and get the length required. * * @param int $length * @return string */
function getRandomStringShuffle($length = 16)
{ $stringSpace = '0123456789abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ'; $stringLength = strlen($stringSpace); $string = str_repeat($stringSpace, ceil($length / $stringLength)); $shuffledString = str_shuffle($string); $randomString = substr($shuffledString, 1, $length); return $randomString;
}
echo "<br>Using shuffle(): " . getRandomStringShuffle();
?>
4) Using bin2hex()
Like random_int(), the random_bytes() returns cryptographically secured random bytes.
If the function doesn’t exists, this program then uses openssl_random_pseudo_bytes() function.
<?php
/** * Get bytes of using random_bytes or openssl_random_pseudo_bytes * then using bin2hex to get a random string. * * @param int $length * @return string */
function getRandomStringBin2hex($length = 16)
{ if (function_exists('random_bytes')) { $bytes = random_bytes($length / 2); } else { $bytes = openssl_random_pseudo_bytes($length / 2); } $randomString = bin2hex($bytes); return $randomString;
}
echo "<br>Using bin2hex(): " . getRandomStringBin2hex();
?>
5) Using mt_rand()
PHP mt_rand() is the replacement of rand(). It generates a random string using the Mersenne Twister Random Number Generator.
This code generates the string base dynamically using the range() function.
Then, it runs the loop to build the random string using mt_rand() in each iteration.
<?php
/** * Using mt_rand() actually it is an alias of rand() * * @param int $length * @return string */
function getRandomStringMtrand($length = 16)
{ $keys = array_merge(range(0, 9), range('a', 'z')); $key = ""; for ($i = 0; $i < $length; $i ++) { $key .= $keys[mt_rand(0, count($keys) - 1)]; } $randomString = $key; return $randomString;
}
echo "<br>Using mt_rand(): " . getRandomStringMtrand();
?>
6) Using hashing sha1()
It applies sha1 hash of the string which is the result of the rand().
Then, it extracts the substring from the hash with the specified length.
<?php
/** * * Using sha1(). * sha1 has a 40 character limit and always lowercase characters. * * @param int $length * @return string */
function getRandomStringSha1($length = 16)
{ $string = sha1(rand()); $randomString = substr($string, 0, $length); return $randomString;
}
echo "<br>Using sha1(): " . getRandomStringSha1();
?>
7) Using hashing md5()
It applies md5() hash on the rand() result. Then, the rest of the process are same as the above example.
<?php
/** * * Using md5(). * * @param int $length * @return string */
function getRandomStringMd5($length = 16)
{ $string = md5(rand()); $randomString = substr($string, 0, $length); return $randomString;
}
echo "<br>Using md5(): " . getRandomStringMd5();
?>
8) Using PHP uniqid()
The PHP unigid() function gets prefixed unique identifier based on the current time in microseconds.
It is not generating cryptographically random number like random_int() and random_bytes().
<?php
/** * * Using uniqid(). * * @param int $length * @return string */
function getRandomStringUniqid($length = 16)
{ $string = uniqid(rand()); $randomString = substr($string, 0, $length); return $randomString;
}
echo "<br>Using uniqid(): " . getRandomStringUniqid();
?>










Share this page