by
Vincy. Last modified on June 17th, 2022.
The jsPDF AutoTables plugin is for converting a table to a PDF. This is a dependable client-side library to generate reports online in a table format.
It has many features around the PDF generation process using this library. It supports customizing the appearance by defining table column structure and styles.
In this article, we will see the capability of this plugin and its usage with examples.
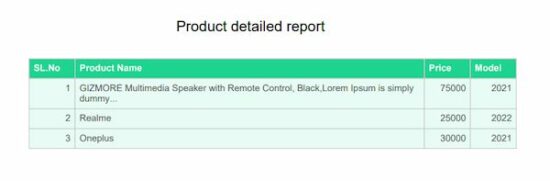
The below code shows a quick example to learn how to use the jsPDF autoTable library to convert tabular data into a PDF.
It builds the options array to specify a body, start position and more to create a PDF document. It outputs a PDF document as a result and prompts to download it to the browser.
Quick example
window.onload = function() { var doc = new jsPDF('p', 'pt', 'letter') // Supply data via script var body = [ ['SL.No', 'Product Name', 'Price', 'Model'], [1, 'I-phone', 75000, '2021'], [2, 'Realme', 25000, '2022'], [3, 'Oneplus', 30000, '2021'], ] // generate auto table with body var y = 10; doc.setLineWidth(2); doc.text(200, y = y + 30, "Product detailed report"); doc.autoTable({ body: body, startY: 70, theme: 'grid', }) // save the data to this file doc.save('auto_table_with_javascript_data');
}
Basics of jsPDF Autotable
This plugin can receive two types of source formats for generating a standard PDF.
- An array of table row data to supply via script.
- HTML table element object to parse for converting a table to PDF.
How to integrate?
There are many ways to integrate this library into an application. Those are listed below.
- Using npm command as like
npm install jspdf jspdf-autotable
- Download the plugin library from Github.
- Include jsPDF and jsPDF Autotable via CDN URL.
https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/jspdf/2.5.1/jspdf.umd.min.js https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/jspdf-autotable/3.5.25/jspdf.plugin.autotable.min.js
Features
This list shows some of the widely used features of the jsPDF AutoTables plugin. Other than that, it has more features that can be found in the official documentation page.
- It provides options to set table content with html, head, body, foot, columns. The html and body are required among them.
- It provides more control over table cells and columns using CellDef and ColumnDef properties.
- It has built-in themes for tables and also allows adding custom styles.
- It provides hooks to callback on an event basis. This callback passes the hookData reference.
Database script
The below SQL script is used for having the backend data for the PDF table source. Import this SQL before running the AutoTable examples using database data to Generate PDF.
It helps to load dynamic data into the HTML table.
- This HTML source will be used as a reference with the Autotable.html property.
- This data can also be converted as a JSON object and mentioned in the Autotable.body property to Generate PDF.
structure.sql
--
-- Table structure for table `tbl_product`
-- CREATE TABLE `tbl_product` ( `id` int(11) NOT NULL, `product_name` varchar(255) NOT NULL, `price` varchar(255) NOT NULL, `model` varchar(255) NOT NULL
); --
-- Dumping data for table `tbl_product`
-- INSERT INTO `tbl_product` (`id`, `product_name`, `price`, `model`) VALUES
(1, 'GIZMORE Multimedia Speaker with Remote Control, Black', '2300', '2020'),
(2, 'Black Google Nest Mini', '3400', '2021'),
(3, 'Black Digital Hand Band, Packaging Type: Box', '1800', '2019'),
(4, 'Lenovo IdeaPad 3 Intel Celeron N4020 14\'\' HD ', '29490', '2021'),
(5, 'JBL Airpods', '2300', '2020'),
(6, 'Black Google Nest Mini', '3400', '2021'),
(7, 'Black Digital Hand Band, Packaging Type: Box', '1800', '2019'),
(8, 'Lenovo IdeaPad 3 Intel Celeron N4020 14\'\' HD ', '29490', '2021'); ALTER TABLE `tbl_product` ADD PRIMARY KEY (`id`); ALTER TABLE `tbl_product` MODIFY `id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, AUTO_INCREMENT=11;
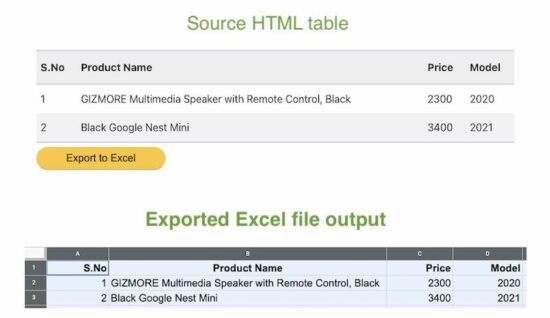
Simple HTML Table to PDF generation using jsPDF AutoTables
The PDF table data is dynamic from the database. The below code fetches the database records and display them in the UI with a HTML table.
It also shows a button to trigger the PDF generation on clicking it.
The on click event calls a JavaScript function named generateTable(). It refers to HTML table in the UI in the AutoTable.html option.
html-to-pdf-using-jspdf.php
<?php
namespace Phppot; require_once __DIR__ . '/lib/DataSource.php';
$conn = new DataSource();
$sql = "SELECT * FROM tbl_product";
$result = $conn->select($sql);
?>
<html>
<title>Product</title>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/jspdf/1.5.3/jspdf.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/jspdf-autotable/3.5.6/jspdf.plugin.autotable.min.js"></script>
<script src="assets/js/jspdf-autotable-custom.js"></script>
<link href="assets/css/style.css" rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" />
</head>
<body> <div class="container"> <h2 class="text-center heading">Product detailed list</h2> <table class="table" id="product-table"> <tr class="border"> <th class="text-align">SL.No</th> <th>Product Name</th> <th class="text-align">Price</th> <th class="text-align">Model</th> </tr> <?php if (! empty($result)) {?> <?php foreach ($result as $k=>$val) {?> <tr class="content border"> <td class="text-align"><?php echo $result[$k]["id"];?></td> <td class="border-dark"><?php echo $result[$k]["product_name"];?></td> <td class="text-align"><?php echo $result[$k]["price"];?></td> <td class="text-align"><?php echo $result[$k]["model"];?></td> </tr> <?php }}?> </table> <input type="button" class="export-button" onclick="generateTable()" value="Generate PDF" /> </div>
</body>
</html>
Generate PDF from HTML table using AutoTable function
This script shows the generateTable() function and prepares the title and the table data to display in the PDF.
The autoTable() function uses the HTML table’s id selector reference to get the table data for the PDF.
Also, it fixes the PDF starting coordinates, themes and styles with the reference of the jsPDF instance.
By parsing the HTML table source, it outputs a PDF document that can be downloaded and saved.
function generateTable() { var doc = new jsPDF('p', 'pt', 'letter'); var y = 20; doc.setLineWidth(2); doc.text(200, y = y + 30, "Product detailed report"); doc.autoTable({ html: '#product-table', startY: 70, theme: 'grid', columnStyles: { 0: { halign: 'right', tableWidth: 100, }, 1: { tableWidth: 100, }, 2: { halign: 'right', tableWidth: 100, }, 3: { halign: 'right', tableWidth: 100, } }, }) doc.save('auto_table_pdf');
}
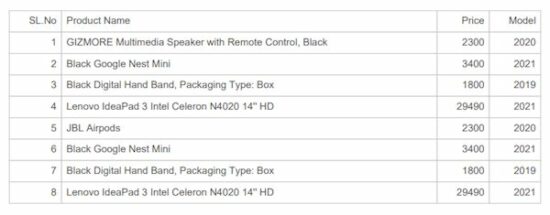
Set default theme and custom styles for PDF tables
The jsPDF AutoTable plugin provides built-in themes. The possible values are ‘stripped’, ‘grid’, ‘plain’ and ‘css’.
It also supports adding custom styles by changing the plugin’s default options.
This example uses this plugin to customize the output PDF appearance by applying exclusive styles. These styles are applied on top of the configured theme appearance.
pdf-with-plugin-theme-and-custom-styles.php
<html>
<title>Product</title>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/jspdf/1.5.3/jspdf.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/jspdf-autotable/3.5.6/jspdf.plugin.autotable.min.js"></script>
<link href="assets/css/style.css" rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" />
</head>
<body> <div class="container"> <input type="button" class="export-button" onclick="setThemeCustomStyle();" value="Generate PDF" /> </div>
</body>
</html>
The autoTable sets PDF table theme as grid and applies custom styles using headStyles and columnStyles options.
The custom styles override the cell background color, height and other default settings.
function setThemeCustomStyle() { var doc = new jsPDF('p', 'pt', 'letter') // generate the above data table var body = [ [1, 'GIZMORE Multimedia Speaker with Remote Control, Black,Lorem Ipsum is simply dummy...', 75000, '2021'], [2, 'Realme', 25000, '2022'], [3, 'Oneplus', 30000, '2021'], ] // New Header and Footer Data Include the table var y = 10; doc.setLineWidth(2); doc.text(200, y = y + 30, "Product detailed report"); doc.autoTable({ body: body, startY: 70, head:[['SL.No', 'Product Name', 'Price', 'Model']], headStyles :{lineWidth: 1,fillColor: [30, 212, 145],textColor: [255,255,255], }, theme: 'grid', columnStyles: { 0: { halign: 'right', cellWidth: 50, fillColor: [232, 252, 245], }, 1: { halign: 'left', cellWidth: 380, fillColor: [232, 252, 245], }, 2: { halign: 'right', cellWidth: 50, fillColor: [232, 252, 245], }, 3: { halign: 'right', cellWidth: 50, fillColor: [232, 252, 245], } }, }) // save the data to this file doc.save('auto_table_theme_custom_styles');
}
Create a PDF table with a header and footer
When preparing reports in a tabular format, the header, and footer components are most probably required. The header is for classifying the column data with keys or categories.
The footer components’ purpose commonly depends on the type of tabular report. If the table is huge in length, the footer may duplicate the header columns. If the table contains statistical data, the footer may reflect the consolidated figures.
In this way, the header and footer give value-add to the tabular report.
This plugin gives various methods to add header and footer parts along with the table body. Two of them are taken here for implementation in the below examples.
- Using head and foot properties
- Using column properties
Using head and foot properties
The page will contain a “Generate” button to call the below JavaScript function. This function initiates autoTable and specify the following properties.
- body
- head
- foot
- headStyles
- footStyles
- columnStyles
Then, To press the export button it not only downloads the table but also shows the table along with the header footer data value that we have added.
jspdf-long-text-header-footer.php
function generateHeaderFooterTable() { var doc = new jsPDF('p', 'pt', 'letter') // generate the above data table var body = [ [1, 'GIZMORE Multimedia Speaker with Remote Control...', 75000, '2021'], [2, 'Realme', 25000, '2022'], [3, 'Oneplus', 30000, '2021'], ] // New Header and Footer Data Include the table var y = 10; doc.setLineWidth(2); doc.text(200, y = y + 30, "Product detailed report"); doc.autoTable({ body: body, startY: 70, head:[['SL.No', 'Product Name', 'Price', 'Model']], foot:[[' ', 'Price total', '130000', ' ']], headStyles :{textColor: [255, 255, 255],}, footStyles :{textColor: [255, 255, 255],}, theme: 'grid', columnStyles: { 0: {halign: 'right', cellWidth: 50,}, 1: {halign: 'left', cellWidth: 380,}, 2: {halign: 'right', cellWidth: 50,}, 3: {halign: 'right', cellWidth: 50,} }, }) ...
... // save the data to this file doc.save('auto_table_header_footer');
}
Using column properties
Using this method, it maps the data key-value pair in the body of the autoTable specification.
Then, it specifies the column name in the header with the corresponding key reference used in the body.
It allows adding styles to the table columns with the columnStyles property. In the below example, it aligns the price column data to the right by setting halign in the columnStyles.
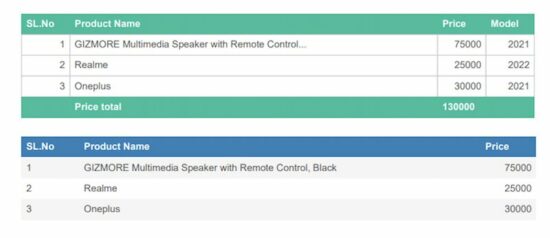
doc.autoTable({ columnStyles: { price: { halign: 'right' } }, body: [ { s_no: '1', product_name: 'GIZMORE Multimedia Speaker with Remote Control, Black', price: '75000' }, { s_no: '2', product_name: 'Realme', price: '25000' }, { s_no: '3', product_name: 'Oneplus', price: '30000' }, ], columns: [ { header: 'SL.No', dataKey: 's_no' }, { header: 'Product Name', dataKey: 'product_name' }, { header: 'Price', dataKey: 'price' }, ],
})
Create PDF with nested data table
First, the UI will show a parent table using the below HTML code. This example will describe how to add a nested table inside this parent while generating a PDF.
The AutoTable plugin provides various callback functions. This example script uses drawCell function to insert the nested table in the callback.
It helps to add more data via JavaScript to the preliminary level of information displayed on load.
jspdf-nested-autotable.php
<html>
<title>Product</title>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1"> <script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/jspdf/1.5.3/jspdf.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/jspdf-autotable/3.5.6/jspdf.plugin.autotable.min.js"></script>
<link href="assets/css/style.css" rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" />
<script src="assets/js/jspdf-autotable-custom.js"></script>
</head>
<body> <div class="container"> <h2 class="text-center heading">Product detailed list</h2> <table class="table" id="product-table"> <tr class="content border border-dark"> <td>iPhone</td> <td>Version: 13</td> </tr> </table> <input type="button" class="export-button" onclick="generateNestedPdf()" value="Generate PDF" /> </div>
</body>
</html>
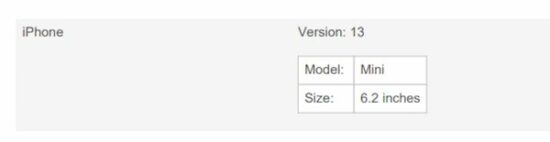
The below script refers to the HTML table object to generate the parent table in the PDF. Then, it defines a callback to insert sub information in a child table.
This child table is inserted into a cell on a conditional basis. This condition checks the dataKey and the section attribute of the document instance. The custom styles define the cell dimension.
function generateNestedPdf() { var doc = new jsPDF(); doc.autoTable({ html: '#product-table', head: [["Product", "Specification"]], didDrawCell: function (data) { if (data.column.dataKey === 1 && data.cell.section === 'body') { doc.autoTable({ body: [ ["Model: ", "Mini"], ["Size: ", "6.2 inches"] ], startY: data.cell.y + 10, margin: { left: data.cell.x + data.cell.padding('left') }, tableWidth: 'wrap', theme: 'grid', }); } }, columnStyles: {5: {cellWidth: 40}}, bodyStyles: {minCellHeight: 30} }); doc.save('nested_table_pdf');
};
PDF tables with a horizontal page break
This example is very important and useful in a report generation application.
When the loaded table data exceeds the target PDF layer, the table has to be wrapped. It is to prevent the data from being cut off from the PDF boundary.
By enabling the horizontalPageBreak it wraps the table and displays the wrapped content on the next page.
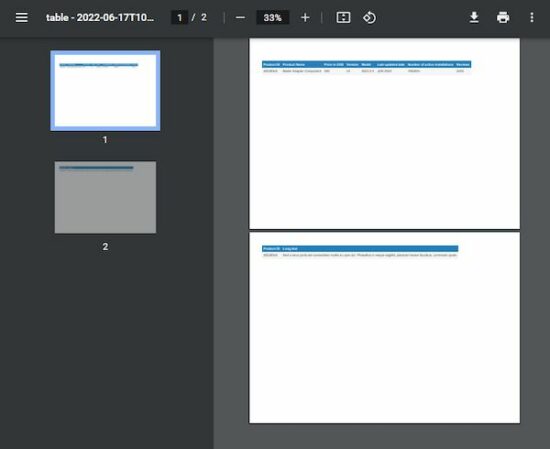
This example shows a 9-column table that wraps the lost column on exceeding the boundary.
It also enables the horizontalPageBreakRepeat to show the mapping for wrapped content with unique column data.
jspdf-horizontal-page-break.php
<html>
<title>Product</title>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/jspdf/2.5.1/jspdf.umd.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/jspdf-autotable/3.5.23/jspdf.plugin.autotable.js"></script>
<link href="assets/css/style.css" rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" />
<body> <div class="container"> <input type="button" class="export-button" onclick="generateHorizontalPageBreak();" value="Export PDF" /> </div>
</body>
</html>
The autoTable sets horizontalPageBreak: true to switch on this feature.
function generateHorizontalPageBreak() { var doc = new jspdf.jsPDF('l') var head = [['Product ID', 'Product Name', 'Price in USD', 'Version', 'Model', 'Last updated date', 'Number of active installations', 'Reviews', 'Long text']] var body = [['2022#3v5', 'Mailer Adapter Component', '300', 'v5', '2022.3.3', 'JUN 2022', '100000+', '3245', 'Sed a risus porta est consectetur mollis eu quis dui. Phasellus in neque sagittis, placerat massa faucibus, commodo quam.']] doc.autoTable({ head: head, body: body, startY: 25, // split overflowing columns into pages horizontalPageBreak: true, // repeat this column in split pages horizontalPageBreakRepeat: 0, })
doc.save('table.pdf');
}
Conclusion
Thus, we have seen various tools in jsPDF AutoTable to create PDF tables. By learning how to convert HTML table to PDF, it will be helpful in a report generation utility of an application.
PDF tables always useful to export statistics or other tabular data from HTML. The source of data can be a database or excel which loaded into HTML tables or converted into an JSON array to parse.
Download
Popular Articles
↑ Back to Top