Payment gateway integration is an important module in building an eCommerce website. For a WooCommerce store, there are several options to integrate a payment gateway.
A payment gateway is to enable an online payment feature at the end of the e-shopping process. There are numerous payment gateway providers that give secured, authentic payment processes via the eCommerce application.
The below list shows some of the examples payment gateway providers for the WooCommerce store.
- PayPal
- Stripe
- AfterPay
- Amazon Pay
- PayFast
- Square and more…
Stripe is one of the best choices that provides good payment services..
Reasons to have Stripe for WooCommerce
First, we will see why Stripe is the best to have this payment option regardless of WooCommerce. Then, we can see the combined advantages of having Stripe in WooCommerce.
Stripe is one of the most widely used payment gateway providers. It is a worldwide popular solution for card payments. It has several advantages and they are,
- Ease of integration and use.
- Reasonable transaction fee and conversion rate.
- Seamless experience with credit or debit card payments.
- Secure payment lifecycle with proper webhook registrations.
Merits of integrating Stripe in WooCommerce
- Accepts all popular credit or debit card payments via web or mobile.
- Embedded inline Stripe payment elements instead of redirecting. It will reduce drop offs and increase the conversion rates.
- By using popular WooCommerce Stripe plugins, it results robust solutions for making payments.
- Possibility for easy upgrading to get latest and additional features.

Methods of integrating Stripe in a WooCommerce store
Various plugins are there to integrate a Stripe payment gateway. Three of them are listed below.
- WooCommerce Stripe Payment Gateway
- Payment Plugins for Stripe WooCommerce
- Accept Stripe Payments
The following sections describe these plugins and show how to use them to set up the Stripe payment.
Note: Before starting integration, get the Stripe API keys.
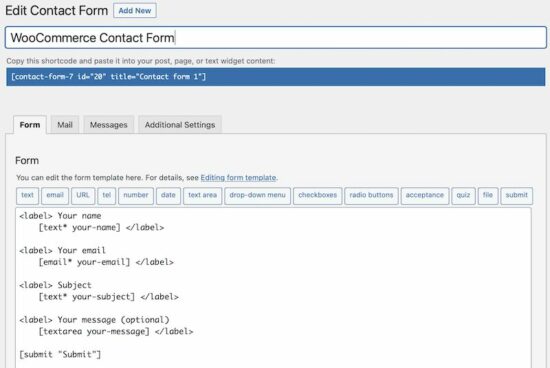
1. WooCommerce Stripe Payment Gateway plugin
This is with the latest possible version and the highest number of active installations. Let’s see its features and advantages below.
| Version | 6.4.0 |
| Active Installations | 900,000+ |
| Last Updated | 1 day ago |
Features
- Accepts majority of the card payments.
- Supports Apple Pay, Google Pay, and Microsoft Pay based on the client.
- Builds an inline Stripe payment with WooCommerce instead of redirecting to the hosted services.
- Supports extensions like WooCommerce Subscriptions.
- Supports connecting Web Payment API to pay via mobile devices.
Advantages
- Keeps track of customer instances and saves time on successive payments.
- Allows quick checkout with touch or face authentication with Apple ID.
- Supports quick payments with a few taps using Web Payment API services.
Steps to integrate
Download this plugin from the official website and unzip it into the WordPress plugin directory. Then, log in to WordPress admin and go to Plugins->Installed Plugins to activate the plugin.
This plugin helps to create a stripe payment in a shopping cart in 2 steps. Click plugin settings and follow the steps below.
- Choose test mode and set up the keys (Publishable, Secret key and Webhook secret key).
- Configure Express Checkout settings. It also allows customizing the Stripe payment element.
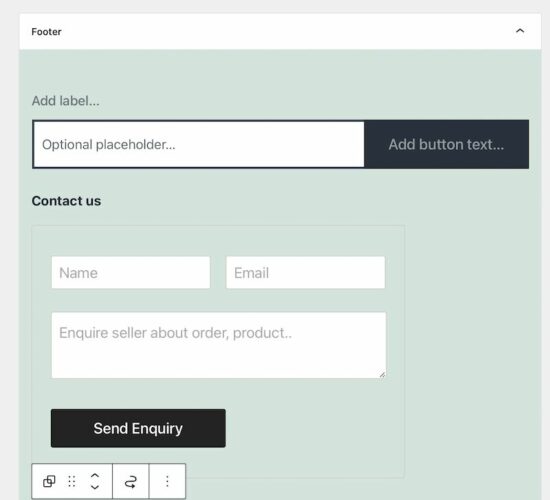
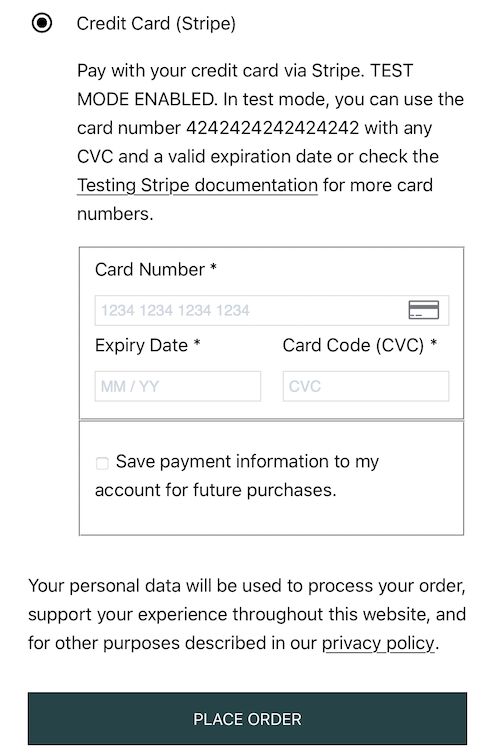
Stripe element in WooCommerce checkout
Once done with the setup, the front-end shop displays the option to checkout with Stripe. The following screenshot shows the Stripe (card only) option on the WooCommerce place-order page.
2. Payment Plugins for Stripe WooCommerce
It supports card payments, mobile payments, direct electronic payments like ACH and more.
It requires WordPress version 5.6 or higher. The key information on the plugin state is shown in the below table.
| Version | 3.3.19 |
| Active Installations | 80,000+ |
| Last Updated | 2 months ago |
Features
- Supports browser payments like Google Pay and Apple Pay in the product, cart, and checkout pages.
- Provides 3D secure 2.0.
- Allows add-ons like WooCommerce Subscriptions, Pre-Orders and Blocks.
Advantages
- It’s an official Stripe partner by which it has high dependability and trustworthiness.
- It has less friction and makes easy seamless payments to increase the conversion rate.
Steps to integrate
Download plugin and set it up in the WordPress shop. Go to plugin settings to configure the Stripe keys and more directives.
The settings page contains many tabs to group the configurations. Let’s see some of the configurations of the plugin settings.
| API Settings | to choose test or live modes. to set Stripe API keys and webhook settings. |
| Advanced Settings | to switch-on installment-based payments. to enable event-based tracking. Example: trigger refund on cancellation; put on hold when a dispute is raised. to enable sending receipts by email. |
| Credit / Debit Cards | to configure Stripe credit card element settings. |
Other than the above, the payments tab has configurations related to the different gateways like Apple Pay and all.
This plugin provides many settings to configure. For the first step configure the following settings to confirm that the Stripe payment has been integrated.
- API key and webhook configuration.
- Stripe card element fields customization.
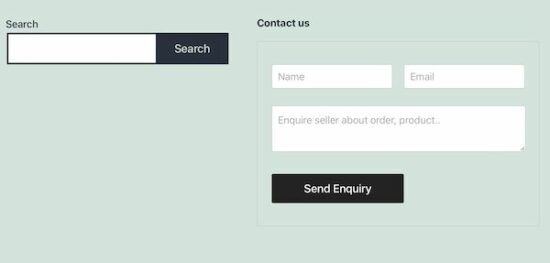
Output Stripe payment option
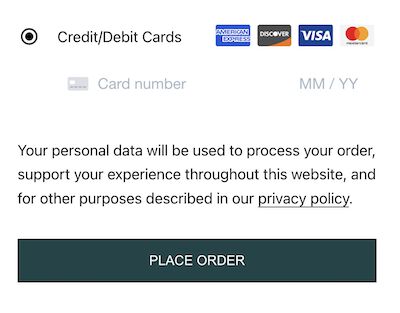
3. Accept Stripe Payments
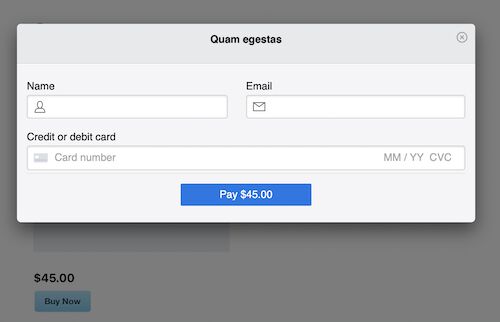
It places Stripe’s ‘Buy Now’ button in the UI. It allows purchasing goods or digital products or services. It embeds the Stripe payment element via shortcode.
It requires WordPress version 5.0 or higher and PHP version 5.6 or higher. It is the second recently updated plugin among the three we have taken for comparison.
| Version | 2.0.63 |
| Active Installations | 40,000+ |
| Last Updated | 1 week ago |
Features
- Provides a single-tap payment solution with a remember me feature.
- Keeps track of the transactions in the WordPress admin.
- Allows selling digital products, media assets and more.
- Allows branding the WooCommerce shop by showing the website logo in the payment window.
- Sends email notification to the buyer and the seller.
- Provides options for future payments with the “Authorize Only” directive.
Advantages
- Renders a responsive Stripe payment panel.
- Allows Stripe element’s customization with CSS to match the WooCommerce theme.
- Gets additional data from the customers using custom fields.
- Secure payment with 3DS authentication and SCA.
Steps to integrate
Download Accept Stripe Payments plugin from the WordPress official repository. Then activate this plugin and configure it to render the Stripe payment option in the WooCommerce front end.
It allows a WordPress website to sell products without WooCommerce. Follow the below steps to configure a preliminary level of Stripe payment settings.
- Open plugin settings and configure API keys.
- Go to Stripe payments -> Products to add ASP products. This step creates the asp-product-shortcode differentiated with the appropriate product id.
- Create a page or post and map the ASP product to be displayed with a Stripe “Buy Now” button.
This plugin has 4 settings tabs classified by having the configurations of Accept Stripe Payments feature.
- General settings
- Email settings
- Advanced settings
- Captcha
General Settings
- When activating this plugin it creates the ‘Thank you’ and ‘ASP product’ pages. The general settings populate these links.
- The product-add action creates the ASP shortcode to be mapped to display the products’ purchase options.
- It contains settings to configure price and currency.
- To enable Billing Zipcode validation to prevent anonymous billing entries.
- Mainly, this tab has the fields to set the Stripe API keys and to toggle between a test or live mode.
Email Settings
- This is to enable sending order receipts via an email notification.
- Configure the target address of the buyer and seller to send the receipt.
- It allows customizing email templates.
Advanced Settings
This tab is used to configure the display element of price, custom fields, terms and more.
- Price settings – to add currency position, decimal point separator, number format with a thousand separator.
- Custom Field Settings – to add options to get extra information for buyers.
Captcha
This plugin strongly recommends enabling captcha to prevent malicious attacks. It provides two types of captcha services.
Conclusion
Since, Stripe payment is a widely used solution, demonstrating payment integration may guide novice and expert developers.
In this article, we have seen three Stripe plugins to set up the payment gateway. The majority of them are WooCommerce plugins.
Also, we saw how to accept payments via a WordPress store without the WooCommerce plugin.
I hope, these choices help to enable the Stripe payment on your WooCommerce website. The wide scope of customization will help to create a unique Stripe element for WooCommerce.