- Ethereum protocol developers plan a new upgrade, called MEV-Burn.
- MEV-Burn will solve the Miner Extractable Value (MEV).
- As a bonus, MEV-Burn will reduce ETH supply on top of the normal burn from EIP-1559 (“The Merge”)
- Developers anticipate a surge in ETH price due to the deflationary shock.
Disclaimer: The author holds securities mentioned in this article.

I just listened to a great podcast on the MEV-burn upgrade, so I thought to contribute a blog post on the topic.

This upgrade addresses the Maximum Extractable Value (MEV) issue and enhances the overall Ethereum ecosystem. The presence of MEV in Ethereum can lead to negative consequences for user experience and network finality. But don’t worry, there’s hope on the horizon with the upcoming MEV-burn upgrade.
In the expanding world of DeFi, MEV has become a growing force in the Ethereum ecosystem, resulting in toxic forms like frontrunning and sandwich attacks, which can be detrimental to transaction originators. The MEV-burn upgrade promises to mitigate these issues and further reduce Ethereum’s circulating supply, ensuring a better experience for users like yourself.
As Ethereum has completed its much-anticipated transition to Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus, the MEV issue becomes even more critical to address. The potential risks include validator centralization and other unforeseen challenges. Thankfully, the MEV-burn upgrade could play a crucial role in safeguarding the network, providing you and the rest of the Ethereum community with more confidence in its security and long-term stability.
Let’s start with a quick overview of the proposal — don’t worry if you don’t get it yet but keep reading. You’ll be smarter afterward! 
High-Level Overview
The MEV-Burn proposal aims to reduce proposer centralization, make validator rewards smoother, and enable MEV smoothing for all ETH holders. It allows Ether to capture on-chain value and enhances its economic attributes by making ETH the currency for block building and protecting its monetary premium. MEV burning results in ETH burn of equivalent value for any extracted opportunity, regardless of the assets involved.

In this system, each validator has a chance to become an eligible proposer for a slot. The average number of eligible proposers per slot can bid to propose the next block. These bids determine how much ETH must be burned by the chosen execution block.
Proposers will likely bid up to the MEV amount, resulting in most MEV being burned. The protocol doesn’t measure MEV directly but allows a burn auction to occur every slot.
The proposal involves increasing slot time to 16 seconds, with the first 4 seconds as a “bidding period.” During this time, eligible proposers submit bids, committing to an execution block hash that must burn ETH equal to their bid.
After bidding ends, the slot proceeds, and the highest bidder reveals their block. Other bidders can also reveal blocks, but higher bidders’ blocks will be prioritized.

ETH protocol developer Justin Drake argues that the MEV Burn will have a significant impact on the number of ETH burned. It could essentially double the deflationary rate, i.e., burning 200k-400k ETH more per year on a current supply of roughly 120M ETH. This could add an additional deflationary “yield” of 0.2% per year!
For a scarce asset like ETH, the MEV-Burn could mean an absolute supply shock. In a bull market with lots of demand that would lead to exploding prices. 


Wen MEV Burn? 

If you’re wondering when the MEV burn will be hard-forked into the Ethereum chain, here’s my best guess based on people more credible than me:
In a recent bankless podcast interview, the Ethereum protocol researcher Justin Drake estimated that the MEV-Burn upgrade will take three to five years. If you take the average and adjust for unforeseen protocol issues, you should not expect MEV burn to come into effect before May 2027.
Understanding MEV and Ethereum

Ethereum Ecosystem
In the Ethereum ecosystem, a key concept you should know is MEV, or Maximal Extractable Value.
MEV is the amount of profit that miners, validators, and block builders can extract from a block by rearranging or including certain transactions. This can impact transaction costs, causing higher gas fees and delays for regular users like yourself.
 Recommended: Introduction to Ethereum’s Gas in Solidity Development
Recommended: Introduction to Ethereum’s Gas in Solidity Development
MEV in Decentralized Finance
The concept of MEV has become more prominent with the explosion of DeFi (Decentralized Finance) in 2020 — and particularly with the merge, i.e., the move towards proof-of-stake consensus.
 Recommended: Common Consensus Mechanisms in Blockchains
Recommended: Common Consensus Mechanisms in Blockchains
In DeFi, various financial applications are built on top of blockchain networks like Ethereum. MEV plays a crucial role in these applications, as it can affect transaction costs and user processing times.
Toxic forms of MEV, such as frontrunning and sandwich attacks, can result in negative settlements, which means you, the transaction originator, may face disadvantages when trading on DeFi platforms such as Uniswap.
I highly recommend you check out our academy course on Uniswap and DeFi if you plan to get a job in crypto — it’s fun and very profitable! 
 Academy Course: Uniswap Automated Finance for Blockchain Engineers
Academy Course: Uniswap Automated Finance for Blockchain Engineers
MEV Participants and Opportunities
The main participants involved with MEV are validators and block builders. These entities are responsible for securing the Ethereum network, validating transactions, and building new blocks. By leveraging MEV opportunities, these participants can increase their revenue.
For example:
- Miners: They
- Validators: Validators can reorder, include, or exclude transactions in a block to maximize their profits, i.e., rearranging transactions to benefit from MEV.
- Block builders: In a PoS (Proof of Stake) model, block builders can also extract value from MEV by optimizing transaction ordering.
Transaction Frontrunning Example (MEV)
An example of Ethereum MEV is when a validator reorders transactions to make a profit. For instance, a validator can extract MEV by reordering transactions in a way that benefits them financially.
Suppose a user wants to trade 1 ETH for 100 DAI, and another user wants to trade 1 ETH for 200 DAI. The validator can re-order the transactions so that the second user’s trade is executed first, and then the first user’s trade.
By doing so, the validator can extract the price difference between the two trades, which is 100 DAI, as a profit.
This practice is known as “transaction frontrunning” and is a common way for validators to extract MEV (source: CoinDesk).
Impact of MEV on Gas Prices and Transactions

EIP-1559 and Gas Prices
With the introduction of EIP-1559, Ethereum aimed to make gas price estimation more predictable for users. However, it is essential to consider MEV’s influence on gas prices. When MEV bots attempt to extract value from transactions, they can drive up the gas prices in two ways:
- MEV bots pay higher gas fees to prioritize their transactions, creating a competitive market for the limited block space.
- Non-MEV users also pay higher fees to place their transactions above MEV-extracted transactions, leading to a chain reaction.
This situation might result in an unexpected spike in transaction fees for Ethereum users, even with EIP-1559 in place.
MEV Bots and Network Congestion
MEV bots compete with each other to extract value from user transactions. In times of high network activity, they can contribute to network congestion. MEV bots flood the network with transactions, hoping to exploit profitable opportunities.
In turn, this creates the following scenarios:
- Longer transaction confirmation times
- An increase in the number of pending or dropped transactions
- Overall decline in the network’s performance
These factors affect the user experience for all Ethereum users, making it less predictable and, potentially, less efficient.
 But it seems like MEV is a phenomenon that just comes with any complex monetary system and we just have to accept it. MEV burning at least attempts to use the energy to fuel the economic value of the ETH token.
But it seems like MEV is a phenomenon that just comes with any complex monetary system and we just have to accept it. MEV burning at least attempts to use the energy to fuel the economic value of the ETH token.
Transaction Discrimination in MEV
One significant concern related to MEV is transaction discrimination.
MEV bots often target high-value transactions, such as those involving DeFi protocols or large trades. As a result, if your transaction falls into this category, it might be targeted and front-run by MEV bots. Also, MEV bots might sandwich your transaction, potentially causing you to receive a worse deal.
If your transaction is not considered valuable by MEV bots, they might still impact your experience indirectly.
For example, because of the increased gas prices and network congestion caused by MEV bots, your transaction might still be delayed or require higher transaction fees.
MEV-Burn: A Solution to MEV Issues

MEV-Smoothing Concept
As you dive into Ethereum, you’ll come across the concept of Maximal Extractable Value (MEV). Again, MEV refers to the profits derived from exploiting the ordering of transactions on the blockchain. The MEV-Smoothing concept aims to distribute these profits more fairly across the Ethereum ecosystem.
This innovative idea introduces mechanisms to “smooth” the revenues generated from MEV, ensuring that all participants, including ETH holders and mining pools, can benefit from the value being extracted from the network. It takes a collective approach to address the negative impacts of MEV and creates a more equitable environment for everyone involved.
Proposer-Builder Separation
As Ethereum transitions towards proof-of-stake (PoS) and staking, the proposer-builder separation is one of the key concepts introduced to help mitigate MEV-related issues.
Currently, miners have the power to both create and validate blocks, often leading to frontrunning and other malicious practices that exploit MEV.
With the proposer-builder separation, these roles are effectively split. Proposers become responsible for aggregating transactions and proposing blocks, while builders focus on executing and validating them. This separation reduces the ability of miners to exploit MEV, increasing fairness and trust in the Ethereum ecosystem.
Reducing MEV Profits and Sell Pressure
The introduction of MEV-burn aims to further align the incentives of individual miners with the rest of the Ethereum ecosystem. This innovative upgrade creates a mechanism to burn the MEV profits extracted by miners, reducing the sell pressure on ETH’s price and ultimately benefiting ETH holders.
As mining pools and stakers see their MEV profits channeled back into the system, they can expect a more equitable distribution of rewards. This process, in turn, helps strengthen the entire Ethereum ecosystem by curbing the negative effects of MEV and enabling a more sustainable growth trajectory for the network.
In conclusion, the implementation of MEV-burn, proposer-builder separation, and Mev-Smoothing concepts contribute significantly to addressing the MEV issue in Ethereum. By fostering a more equitable distribution of profits and reducing the ability of miners to exploit MEV, these solutions help ensure a brighter future for the Ethereum ecosystem and its participants.
Exploring Front-Running and Back-Running in MEV

In Ethereum and blockchain technology, front-running and back-running are common issues. As you delve into these topics, it’s important to understand how they can affect users and developers within the ecosystem.
Flashbots and Front-Running Attacks
Front-running occurs when someone—such as a miner or a node—takes advantage of their position within the network to exploit transaction orderings for their own benefit.
 Flashbots are a recent development that aims to address this issue by introducing a fairer environment for all participants. These bots work by transparently allowing searchers to compete for MEV rewards through order flow auctions.
Flashbots are a recent development that aims to address this issue by introducing a fairer environment for all participants. These bots work by transparently allowing searchers to compete for MEV rewards through order flow auctions.
To avoid being a victim of front-running attacks, familiarize yourself with the concept of MEV activity and consider using tools that safeguard your transactions. Keep in mind that Ethereum developers are already addressing this issue through various mempool design improvements.
Back-Running and Chain Reorgs
Back-running, on the other hand, involves the execution of concurrent transactions that aim to capitalize on another user’s desired transaction. It poses a similar threat as front-running and is often tied to chain reorgs where multiple transactions are reorganized within the blockchain.
Knowledge about back-running can help you stay aware of potential risks associated with certain transactions, and may encourage you to engage with projects that actively combat these issues.
The expansion of Flash Boys 2.0 and other efforts focusing on the mitigation of front-running and back-running risks indicates that the Ethereum community is dedicated to addressing these concerns.
Addressing MEV Challenges

The Merge
The Merge has offered new opportunities to address MEV challenges. Ethereum researchers are working on the proposer-builder separation, which separates the role of validators into two distinct functions:
 Proposers: Responsible for creating blocks and providing transaction ordering
Proposers: Responsible for creating blocks and providing transaction ordering Builders: Responsible for collecting and packaging transactions into block candidates
Builders: Responsible for collecting and packaging transactions into block candidates
Separating these roles reduces the risk of validator centralization, and the incentives for harmful actions like eclipse attacks and DDoS attacks are minimized. This new structure will provide a level playing field for all validators, ensuring a healthier network for you and other Ethereum users.
Alternative Solutions to MEV Problems
Ethereum researchers are exploring alternative approaches to address MEV-related problems. One such solution is MEV smoothing.
MEV smoothing involves evenly distributing the MEV revenue to a larger group of participants, preventing any single validator from receiving a disproportionately high reward. This can help reduce validator centralization further and enhance the security of the Ethereum network.
For example, Rocketpool  has already distributed a decentralized staking mechanism with smoothing pool for MEV.
has already distributed a decentralized staking mechanism with smoothing pool for MEV.
Another solution currently under development is the MEV-burn upgrade, which aims to redistribute extracted value to Ethereum users by burning a portion of the MEV rather than passing it to validators. This upgrade is conceptually similar to EIP-1559 and aims to make the Ethereum network more equitable for its users.
Chain reorgs are another MEV-related concern. However, with the Proof-of-Stake model and the proposer-builder separation, the potential for chain reorgs should be significantly reduced. This will help maintain the integrity of the Ethereum network and protect your transactions from being manipulated.
In conclusion, addressing MEV challenges is a priority for Ethereum researchers, and various solutions are being developed to safeguard the network and improve your experience as an Ethereum user.
 Recommended: Ethereum – Top 10 Articles to Get Started
Recommended: Ethereum – Top 10 Articles to Get Started

 (
(
 . Als eines der ersten Beispiele für GPT-4, das vollständig autonom arbeitet, erweitert AutoGPT die Grenzen dessen, was mit KI möglich ist
. Als eines der ersten Beispiele für GPT-4, das vollständig autonom arbeitet, erweitert AutoGPT die Grenzen dessen, was mit KI möglich ist 

 . Beispielsweise kann es die SEO Ihrer Website erheblich verbessern und sie aktiver und professioneller erscheinen lassen
. Beispielsweise kann es die SEO Ihrer Website erheblich verbessern und sie aktiver und professioneller erscheinen lassen 
 .
. .
. .
.
 .
. 
 .
.  Ein Computer mit Internetzugang
Ein Computer mit Internetzugang Python installiert (neueste stabile Version)
Python installiert (neueste stabile Version) Zugang zu GitHub zum Herunterladen des AutoGPT-Repositorys
Zugang zu GitHub zum Herunterladen des AutoGPT-Repositorys ! Um zu beginnen, klonen Sie das AutoGPT-Repository von GitHub:
! Um zu beginnen, klonen Sie das AutoGPT-Repository von GitHub: . Von GitHub:
. Von GitHub: : Setzen Sie AutoGPT als Twitter-Bot ein, der autonom ansprechende Inhalte generiert und veröffentlicht, um Ihre Online-Präsenz auszubauen.
: Setzen Sie AutoGPT als Twitter-Bot ein, der autonom ansprechende Inhalte generiert und veröffentlicht, um Ihre Online-Präsenz auszubauen. : Verbessern Sie Ihre Schreibfähigkeiten, indem Sie AutoGPT für kreative Aufgaben wie Geschichtenerzählen, Artikelverfassen oder sogar Dichten verwenden.
: Verbessern Sie Ihre Schreibfähigkeiten, indem Sie AutoGPT für kreative Aufgaben wie Geschichtenerzählen, Artikelverfassen oder sogar Dichten verwenden. : Überwinden Sie Sprachbarrieren, indem Sie AutoGPT nutzen, um Texte mühelos in mehreren Sprachen zu übersetzen.
: Überwinden Sie Sprachbarrieren, indem Sie AutoGPT nutzen, um Texte mühelos in mehreren Sprachen zu übersetzen. : Unterstützen und helfen Sie Schülern bei ihren Studien, indem Sie AutoGPT als virtuellen Lernbegleiter einsetzen.
: Unterstützen und helfen Sie Schülern bei ihren Studien, indem Sie AutoGPT als virtuellen Lernbegleiter einsetzen. : Rationalisieren Sie Ihren Posteingang, indem Sie AutoGPT beauftragen, E-Mails zu sortieren, wichtige Nachrichten zu kennzeichnen und automatisch auf Routineanfragen zu antworten.
: Rationalisieren Sie Ihren Posteingang, indem Sie AutoGPT beauftragen, E-Mails zu sortieren, wichtige Nachrichten zu kennzeichnen und automatisch auf Routineanfragen zu antworten. : Verbessern Sie Ihr Verständnis komplexer Systeme, indem Sie die Fähigkeit von AutoGPT nutzen, verschiedene Szenarien zu simulieren und zu analysieren.
: Verbessern Sie Ihr Verständnis komplexer Systeme, indem Sie die Fähigkeit von AutoGPT nutzen, verschiedene Szenarien zu simulieren und zu analysieren.
 Empfohlen (Englisch):
Empfohlen (Englisch):  Think of it as having multiple browser tabs open; while one page loads, you can continue browsing other tabs. This capability means your Python applications can become faster, more efficient, and capable of handling many I/O operations.
Think of it as having multiple browser tabs open; while one page loads, you can continue browsing other tabs. This capability means your Python applications can become faster, more efficient, and capable of handling many I/O operations. 



 Recommended:
Recommended: 


 Look no further than Meta’s
Look no further than Meta’s  . It tries to produce content like poetry and stories, much like
. It tries to produce content like poetry and stories, much like 
 However, if your focus is on a particular language, there are other ChatGPT alternatives you could consider like
However, if your focus is on a particular language, there are other ChatGPT alternatives you could consider like  Ressources: Read the paper
Ressources: Read the paper 


 , answer questions, and tell jokes, among other things. By integrating Alpaca into your online projects, you can engage users and attract search engine attention on platforms like Google and Bing
, answer questions, and tell jokes, among other things. By integrating Alpaca into your online projects, you can engage users and attract search engine attention on platforms like Google and Bing 







 .
.  .
. 

 Raven RWKV is an open-source chatbot that may just suit your needs! Developed by BlinkDL, this chatbot is powered by the RWKV language model which uses Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs)
Raven RWKV is an open-source chatbot that may just suit your needs! Developed by BlinkDL, this chatbot is powered by the RWKV language model which uses Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs)  .
.





 This model stands out in applications involving multi-turn dialogues. Thanks to its
This model stands out in applications involving multi-turn dialogues. Thanks to its 













 There are billions of houses but only 21 million Bitcoin — let that sink in.
There are billions of houses but only 21 million Bitcoin — let that sink in.






























 .
.
 .
.


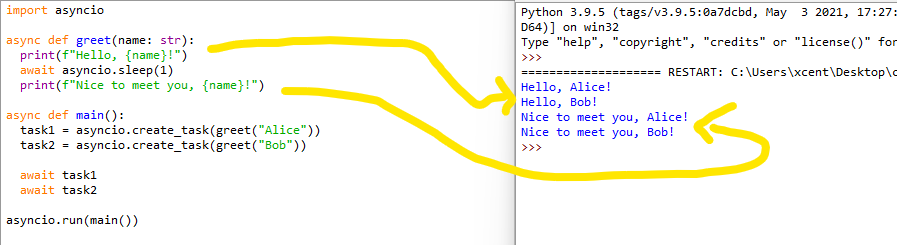
 To recap, here’s the complete code snippet:
To recap, here’s the complete code snippet:
 .
.




